6.2.2 Jumper Wires, BGA Components, Through Board Method
Procedure covers methods for using jumper wires at BGA locations on circuit board assemblies.
Minimum Skill Level: Expert
Conformance Level: High
REQUEST FOR QUOTE GUIDES INDEX

Jumper Wires, BGA Components, Through Board Method
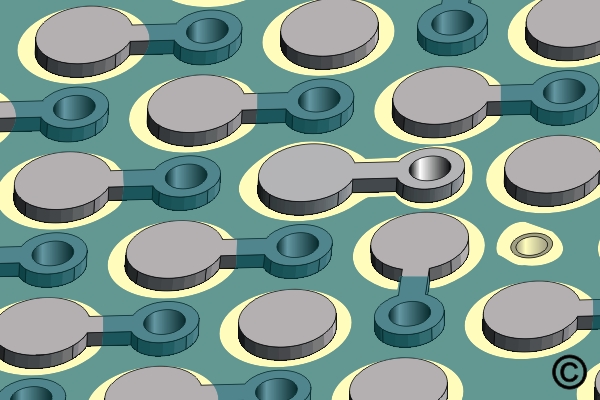
Mill a hole through the board and insert a Teflon sleeve

Insert a copper Circuit Track into the plated hole and Teflon sleeve.

Solder the Circuit Track to the plated hole connected to the BGA pad.

Overcoat the new connection with epoxy.
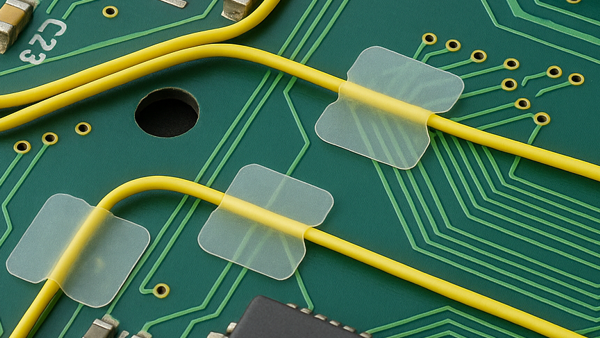
Wire Dots are a thin, flexible polymer film coated on one side with a high-performance, electronics grade permanent pressure-sensitive adhesive.
LEARN MORE
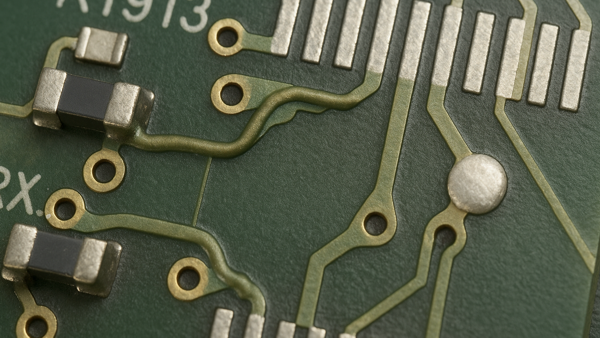
We're here to help with ECO rework, jumper wire adds, circuit cuts, and various complex modifications.
LEARN MORE
SLIDESHOW STARTING
❮
❯