|
Outline
This procedure covers the general guidelines for soldering surface mount J lead components. There is basically only one style of J lead component. Whether leads are on two sides or four sides, or whether the component is large or small, the soldering principles are the same.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Procedure
Procedure
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Images and Figures
Soldering Surface Mount J Lead Components, Continuous Flow Method

Figure 1. Place component and check alignment.
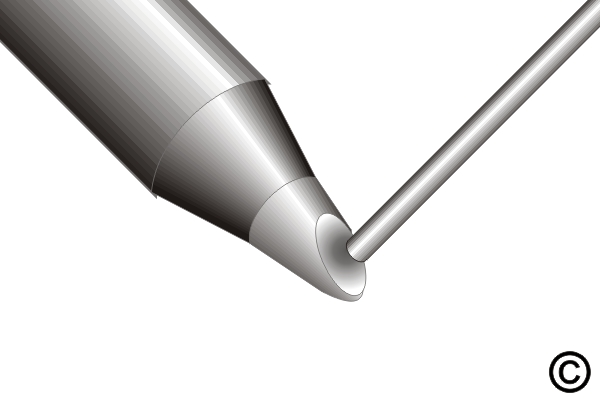
Figure 2. Apply solder to the continuous flow solder tip to create a convex bead of molten solder.

Figure 3. Slowly move the tip over the row of leads to form proper solder fillets at each joint.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
7.4.2 Soldering Surface Mount J Lead Components, Continuous Flow Method
The procedure covers the soldering of surface-mount J-lead components using a continuous-flow soldering method.
Minimum Skill Level: Intermediate
Conformance Level: High
REQUEST FOR QUOTE GUIDES INDEX

Soldering Surface Mount J Lead Components, Continuous Flow Method

Place component and check alignment.

Apply solder to the continuous flow solder tip to create a convex bead of molten solder.

Slowly move the tip over the row of leads to form proper solder fillets at each joint.

Do you need help with surface mount and through-hole component rework or salvage?
LEARN MORE
SLIDESHOW STARTING
❮
❯





