|
Outline
This method is used to replace damaged BGA pads with new dry film adhesive-backed pads. The new pads are bonded to the circuit board surface using a specially designed bonding press or bonding iron. Electrical connection is made to a via circuit which is originally manufactured integral to the pads.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Procedure
Procedure
Evaluation
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Images and Figures
Surface Mount, BGA Pad Repair, Integral Via, Circuit Extension Method

Figure 1. Remove the damaged pad with integral via.

Figure 2. Using a Micro-Drill expose the copper circuit by recessing a trough or gully.

Figure 3. Tin the circuit with solder.

Figure 4. Select a replacement pad that matches the missing pad.

Figure 5. Scrape off the adhesive bonding film from the solder joint connection area on the back of new pad.
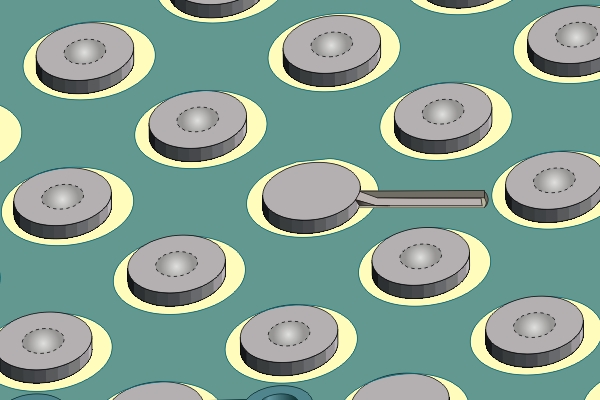
Figure 6. Connecting circuit connected to the exposed and tinned circuit.

Figure 7. Completed repair.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
4.7.5 Surface Mount, BGA Pad Repair, Integral Via, Circuit Extension Method
Procedure covers method to repair damaged BGA pads that have an integral via on circuit board assemblies.
Minimum Skill Level: Expert
Conformance Level: High
REQUEST FOR QUOTE GUIDES INDEX

Surface Mount, BGA Pad Repair, Integral Via, Circuit Extension Method

Remove the damaged pad with integral via.

Using a Micro-Drill expose the copper circuit by recessing a trough or gully.

Tin the circuit with solder.

Select a replacement pad that matches the missing pad.

Scrape off the adhesive bonding film from the solder joint connection area on the back of new pad.

Connecting circuit connected to the exposed and tinned circuit.

Completed repair.

Circuit Frames have a dry-film adhesive backing to ensure the delicate repair procedure is easy, fast, and highly reliable
LEARN MORE

You'll appreciate the accuracy of this precision machine when repairing conductors, lands, and surface mount pads.
LEARN MORE

We're here to help with all your challenging circuit board and electronic component rework and repair needs.
LEARN MORE
SLIDESHOW STARTING
❮
❯