|
Outline
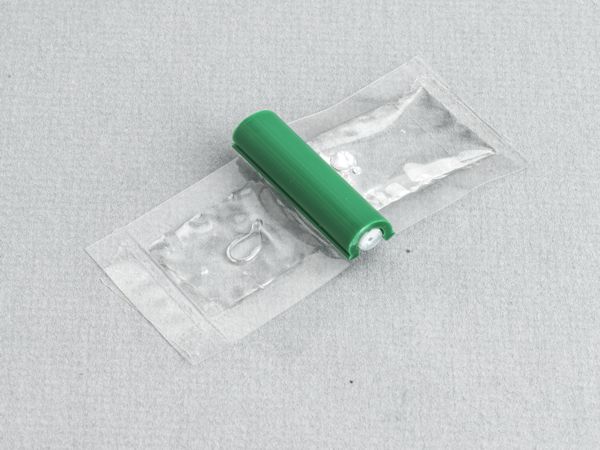
This method replaces solder masks or coatings on circuit boards at BGA locations. BGA locations provide unique challenges due to their inaccessibility after reflow, exposure to high temperatures, and the requirement to surround the BGA pads with masks. The exposed Vias and circuits may cause shorting or BGA solder joint starvation.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Procedure
Evaluation
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Images and Figures
Coating Replacement, Solder Mask, BGA Locations
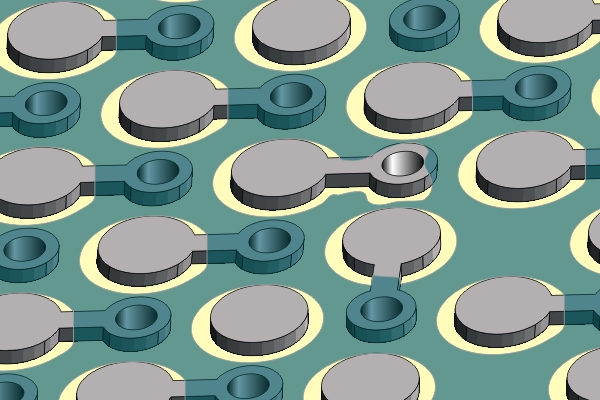
Figure 1. Identify the area(s) with missing solder mask.
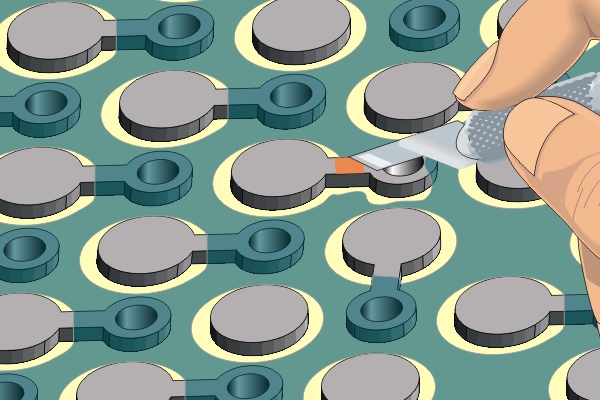
Figure 2. Scrape solder off the "Dog Bone" section between the BGA pad and the connecting via.

Figure 3. Apply the replacement coating to the board surface as required.
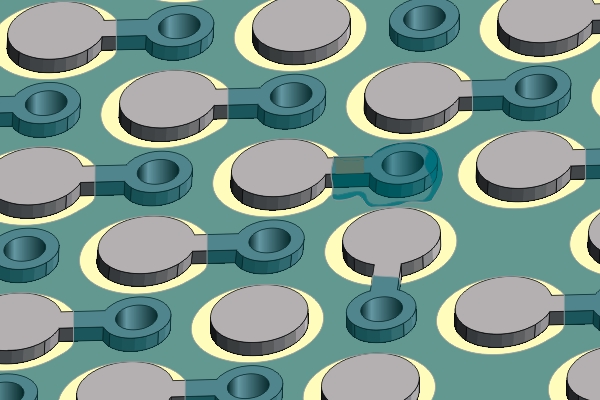
Figure 4. Cure the replacement coating per the manufacturers instructions.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2.4.3 Coating Replacement, Solder Mask, BGA Locations
Procedure covers the methods for replacement of of solder mask on circuit board assemblies at BGA component locations.
Minimum Skill Level: Intermediate
Conformance Level: High
REQUEST FOR QUOTE GUIDES INDEX

Coating Replacement, Solder Mask, BGA Locations

Identify the area(s) with missing solder mask.

Scrape solder off the "Dog Bone" section between the BGA pad and the connecting via.

Apply the replacement coating to the board surface as required.

Cure the replacement coating per the manufacturers instructions.

This clear, low-viscosity, superior-strength epoxy is ideal for many circuit board repair and rework uses.
LEARN MORE
We're here to help with coating removal/replacement and other challenging circuit board rework and repair needs.
LEARN MORE
SLIDESHOW STARTING
❮
❯
















