3.5.1 Base Material Repair, Epoxy Method
Procedure covers minor repair of damaged base board around edges on circuit board assemblies.
Minimum Skill Level: Advanced
Conformance Level: High
REQUEST FOR QUOTE GUIDES INDEX

Base Material Repair, Epoxy Method
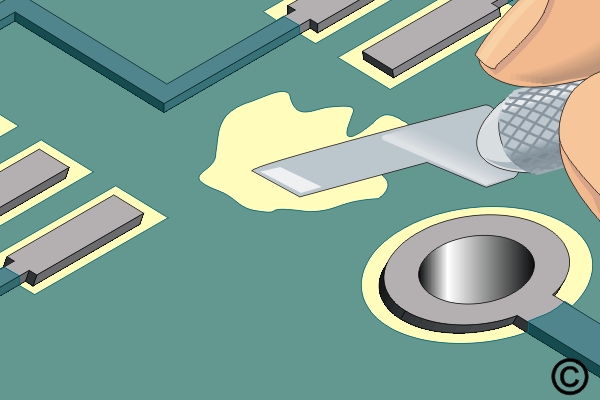
Scrape away damaged base board material with a knife.
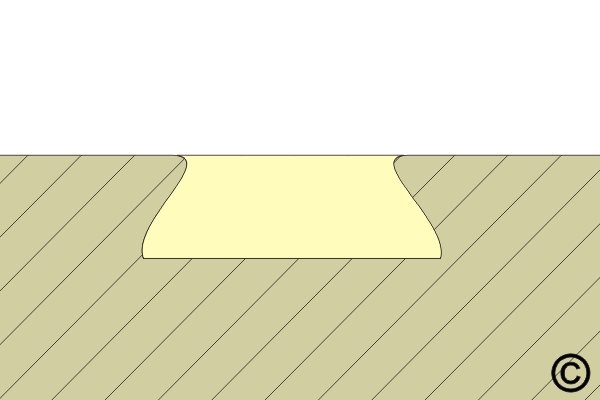
An undercut, to enhance mechanical strength, may be desired for class 3 product.
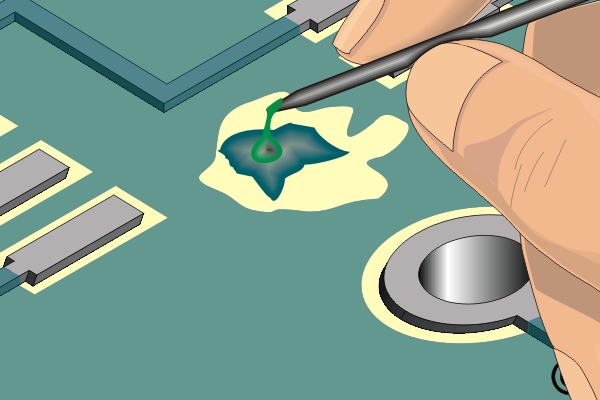
Apply the epoxy with a mixing stick sharpened at the end.

For large areas, apply the epoxy with a foam swab to create a texture.
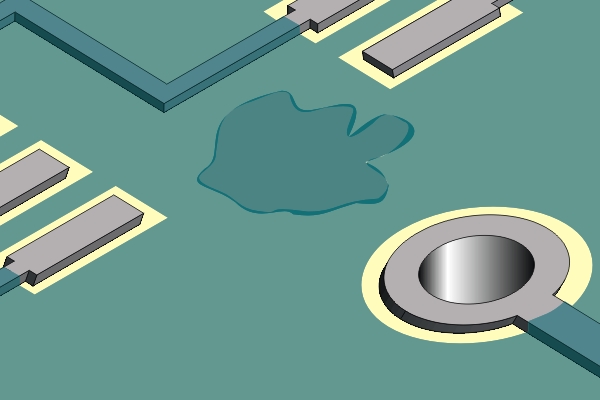
Completed repair.

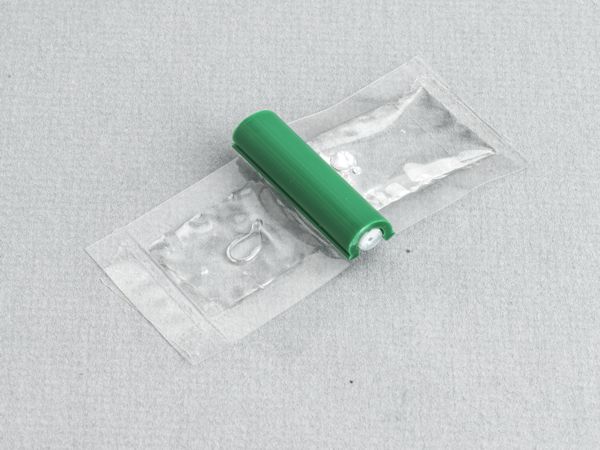
This clear, low-viscosity, superior-strength epoxy is ideal for many circuit board repair and rework uses.
LEARN MORE

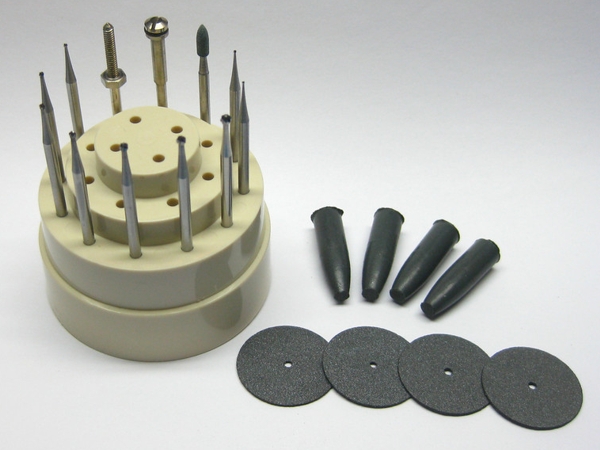
This versatile tool is ideal for milling, drilling, grinding, cutting, and sanding circuit boards.
LEARN MORE
We're here to help with all your challenging circuit board and electronic component rework and repair needs.
LEARN MORE
SLIDESHOW STARTING
❮
❯