3.1 Delamination/Blister Repair, Injection Method
Procedure covers delamination and blister repair on circuit board assemblies.
Minimum Skill Level: Advanced
Conformance Level: High
REQUEST FOR QUOTE GUIDES INDEX

Delamination/Blister Repair, Injection Method
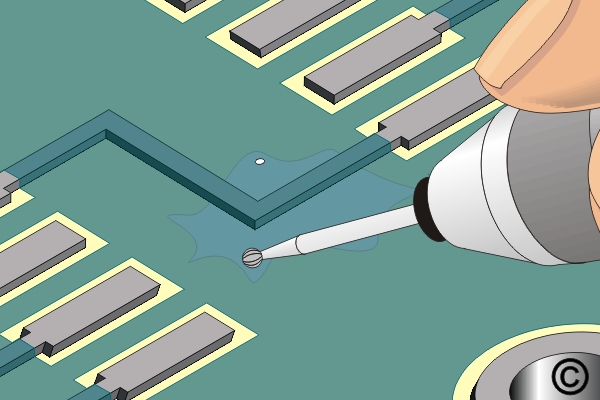
Drill into the delamination blister with the Micro-Drill and ball mill.
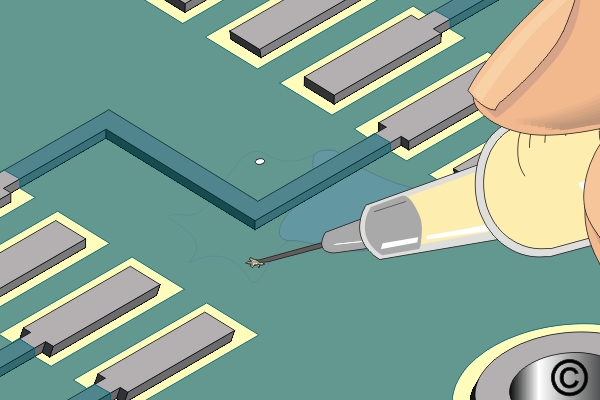
Inject the epoxy into one of the holes in the delamination.
Cure the epoxy per the manufacturer's recommendation.

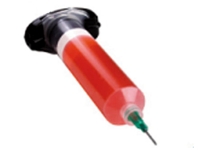
This clear, low-viscosity, superior-strength epoxy is ideal for many circuit board repair and rework uses.
LEARN MORE

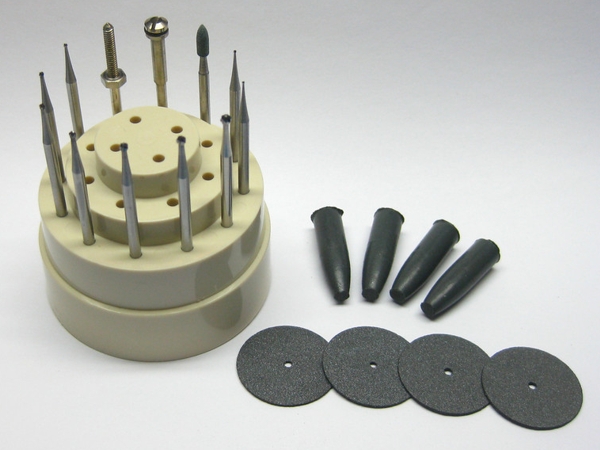
This versatile tool is ideal for milling, drilling, grinding, cutting, and sanding circuit boards.
LEARN MORE

We're here to help with all your challenging circuit board and electronic component rework and repair needs.
LEARN MORE
SLIDESHOW STARTING
❮
❯