|
Outline
This procedure uses a solvent to remove surface coatings. This procedure can be used for spot or overall coating removal of conformal coatings or solder resists. Approved solvents may be used to remove specific soluble-type coatings on a spot basis by brushing or swabbing the local area with the controlled application of solvent until the area is free of the coating material.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Procedure
Local Spot Removal
Overall Removal
Evaluation
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Images and Figures
Coating Removal, Solvent Method
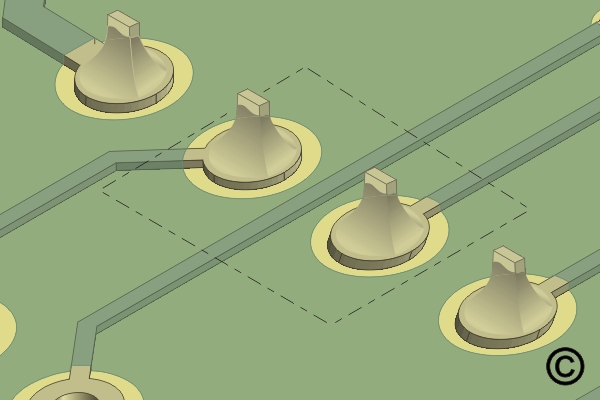
Figure 1. The area requiring coating removal is identified.
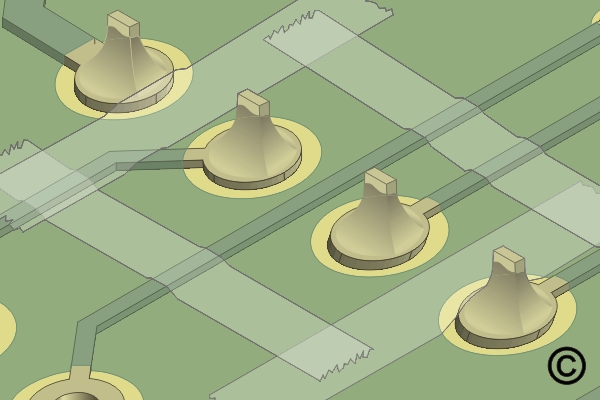
Figure 2. Apply high-temperature tape to outline the area where the coating needs to be removed.

Figure 3. Dip the end of a foam swab in a stripping solution and apply a small amount to the coating to be removed.
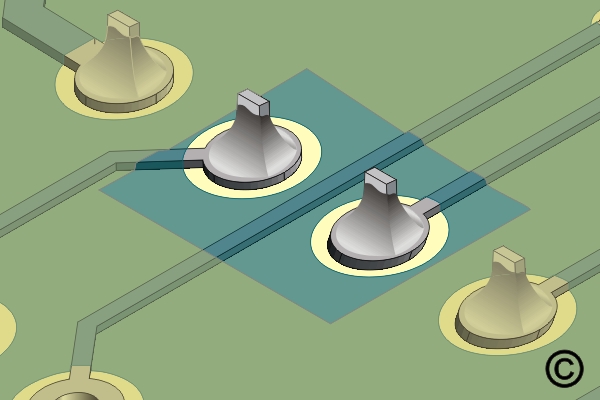
Figure 4. Neutralize or clean the stripped area and dry.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2.3.2 Coating Removal, Solvent Method
Procedure covers the methods for removal of coatings on circuit board assemblies using solvents.
Minimum Skill Level: Advanced
Conformance Level: High
REQUEST FOR QUOTE GUIDES INDEX

Coating Removal, Solvent Method

The area requiring coating removal is identified.

Apply high-temperature tape to outline the area where the coating needs to be removed.

Dip the end of a foam swab in a stripping solution and apply a small amount to the coating to be removed.

Neutralize or clean the stripped area and dry.

This versatile tool is ideal for milling, drilling, grinding, cutting, and sanding circuit boards.
LEARN MORE
We're here to help with coating removal/replacement and other challenging circuit board rework and repair needs.
LEARN MORE
SLIDESHOW STARTING
❮
❯