6.1 Jumper Wires
Procedure covers methods for using jumper wires on circuit board assemblies.
Minimum Skill Level: Intermediate
Conformance Level: High
REQUEST FOR QUOTE GUIDES INDEX

Jumper Wires

See the procedure below for detailed instructions.
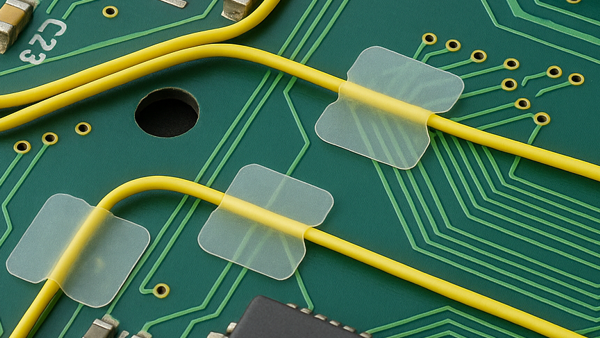
Wire Dots are a thin, flexible polymer film coated on one side with a high-performance, electronics grade permanent pressure-sensitive adhesive.
LEARN MORE
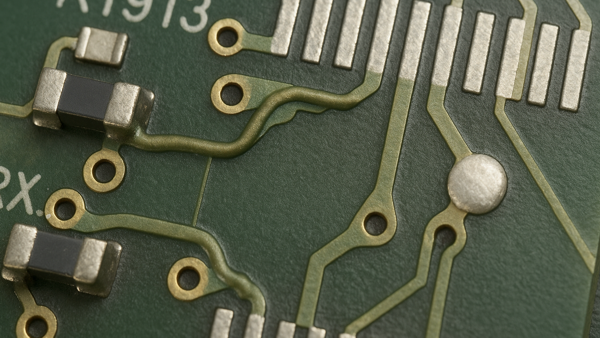
We're here to help with ECO rework, jumper wire adds, circuit cuts, and various complex modifications.
LEARN MORE
SLIDESHOW STARTING
❮
❯

















































