|
Outline
This method is used to replace damaged or missing circuits on internal layers of multilayer circuit boards.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Procedure
Procedure
Evaluation
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Images and Figures
Conductor Repair, Inner Layer Method

Figure 1. Milling into multilayer circuit board to expose the damaged internal circuit.

Figure 2. cut through the base material, one layer at a time, until the desired inner layer has been reached.

Figure 3. Circuit Track in place ready to be soldered.

Figure 4. If spacing is critical or the circuit board uses high frequency circuits, bevel the joint as shown.

Figure 5. Coat the top and sides of the new circuit with epoxy. Add epoxy until flush with top surface.

Figure 6. Completed repair
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
4.2.6 Conductor Repair, Inner Layer Method
Procedure covers repair damaged conductors and circuits on inner layers on circuit board assemblies.
Minimum Skill Level: Expert
Conformance Level: High
REQUEST FOR QUOTE GUIDES INDEX

Conductor Repair, Inner Layer Method

Milling into multilayer circuit board to expose the damaged internal circuit.

cut through the base material, one layer at a time, until the desired inner layer has been reached.

Circuit Track in place ready to be soldered.

If spacing is critical or the circuit board uses high frequency circuits, bevel the joint as shown.

Coat the top and sides of the new circuit with epoxy. Add epoxy until flush with top surface.

Completed repair

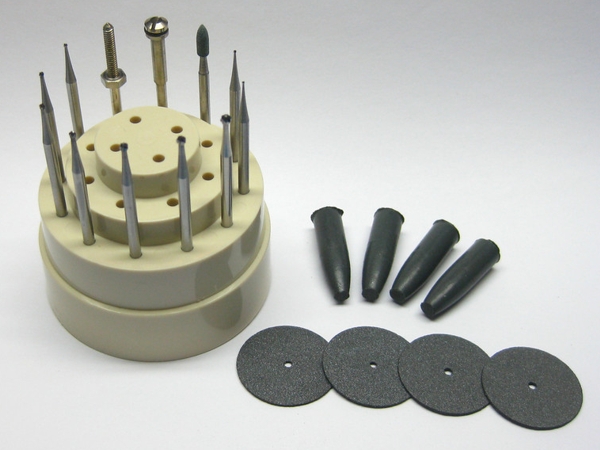
This versatile tool is ideal for milling, drilling, grinding, cutting, and sanding circuit boards.
LEARN MORE

This clear, low-viscosity, superior-strength epoxy is ideal for many circuit board repair and rework uses.
LEARN MORE

We're here to help with all your challenging circuit board and electronic component rework and repair needs.
LEARN MORE
SLIDESHOW STARTING
❮
❯