|
Outline
This method is used on circuit boards to replace damaged or missing circuits on the circuit board surface.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Procedure
Circuit Tracks
Circuit Tracks are rectangular-shaped conductors made of 99.9% pure CDA 11000 copper. These rectangular ribbons closely conform to the original conductor dimensions. The replacement Circuit Track is bonded in place using epoxy.
Evaluation
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Images and Figures
Conductor Repair, Foil Jumper, Epoxy Method
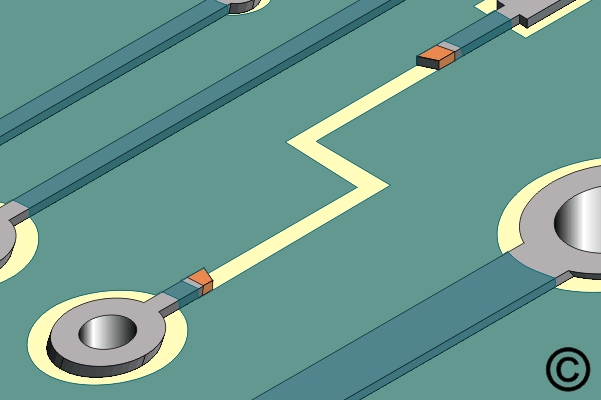
Figure 1. Scrape off any solder mask or coating from the ends of the remaining circuits.
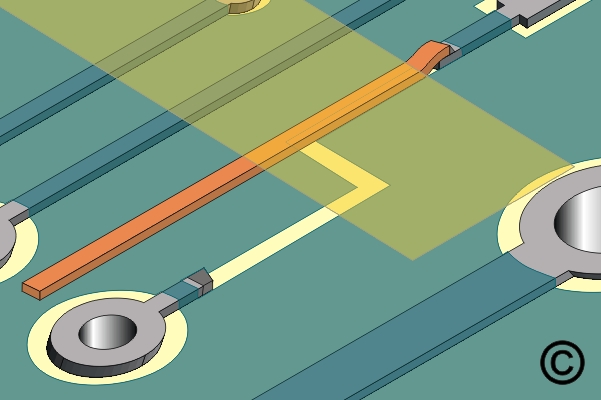
Figure 2. Place the new Circuit Track in position and hold in place with high temperature tape.
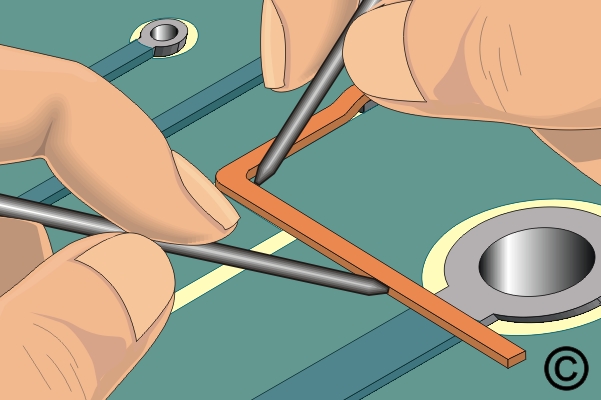
Figure 3. Bend Circuit Track using 2 wood sticks.
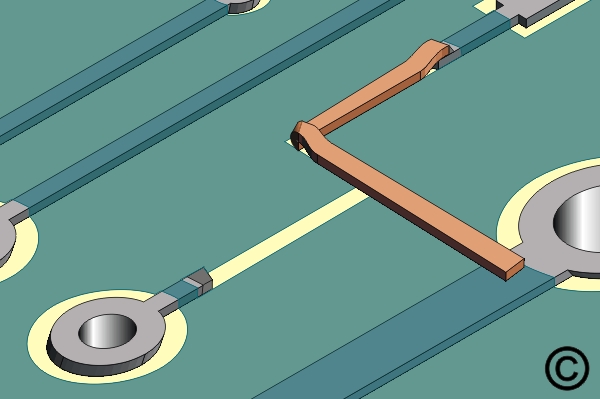
Figure 4. Wide circuits that cannot be easily formed may be folded over to produce a sharp bend.
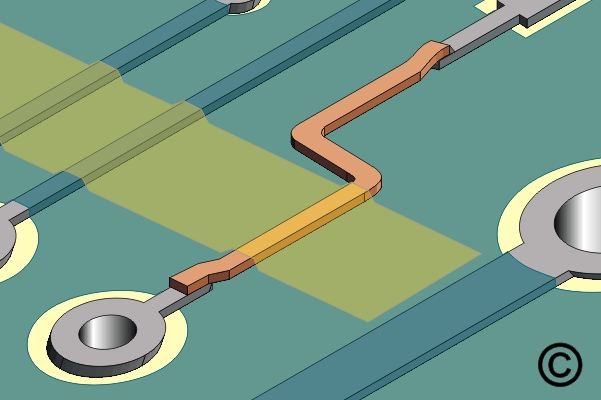
Figure 5. Form the final shape of the Circuit Track then hold in place with high temperature tape while soldering.
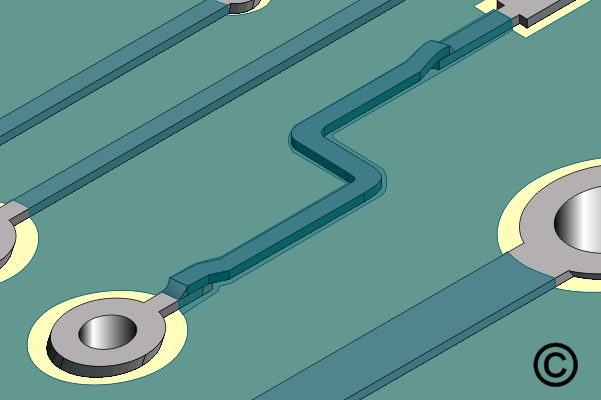
Figure 6. Coat the top and sides of the Circuit Track with epoxy.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
4.2.1 Conductor Repair, Foil Jumper, Epoxy Method
Procedure covers repair of damaged conductors and circuits using liquid epoxy.
Minimum Skill Level: Advanced
Conformance Level: High
REQUEST FOR QUOTE GUIDES INDEX

Conductor Repair, Foil Jumper, Epoxy Method

Scrape off any solder mask or coating from the ends of the remaining circuits.

Place the new Circuit Track in position and hold in place with high temperature tape.

Bend Circuit Track using 2 wood sticks.

Wide circuits that cannot be easily formed may be folded over to produce a sharp bend.

Form the final shape of the Circuit Track then hold in place with high temperature tape while soldering.

Coat the top and sides of the Circuit Track with epoxy.

This clear, low-viscosity, superior-strength epoxy is ideal for many circuit board repair and rework uses.
LEARN MORE

Circuit Frames have a dry-film adhesive backing to ensure the delicate repair procedure is easy, fast, and highly reliable
LEARN MORE

We're here to help with all your challenging circuit board and electronic component rework and repair needs.
LEARN MORE
SLIDESHOW STARTING
❮
❯