|
Outline
This procedure covers the general guidelines for soldering surface mount J lead components. There is basically only one style of J lead component. Whether leads are on two sides or four sides, or whether the component is large or small, the soldering principles are the same.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Procedure
Procedure
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Images and Figures
Soldering Surface Mount J Lead Components, Hot Gas Method
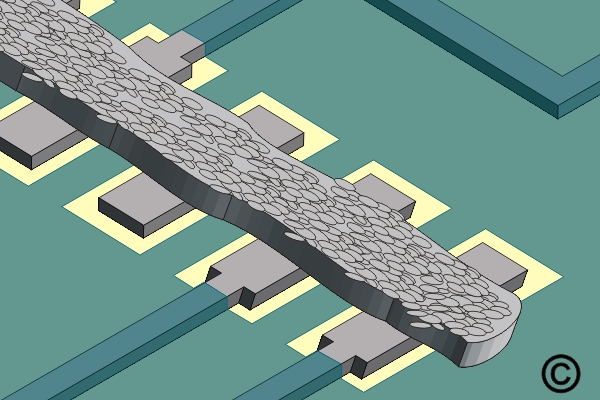
Figure 1. Add a small bead of solder paste along the row of pads.

Figure 2. Move the tool back and forth to heat all the solder joints until complete solder melt is observed.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
7.4.3 Soldering Surface Mount J Lead Components, Hot Gas Method
Procedure covers soldering of surface mount J lead components on circuit board assemblies using a hot gas method.
Minimum Skill Level: Intermediate
Conformance Level: High
REQUEST FOR QUOTE GUIDES INDEX

Soldering Surface Mount J Lead Components, Hot Gas Method

Add a small bead of solder paste along the row of pads.

Move the tool back and forth to heat all the solder joints until complete solder melt is observed.

Do you need help with surface mount and through-hole component rework or salvage?
LEARN MORE
SLIDESHOW STARTING
❮
❯





